
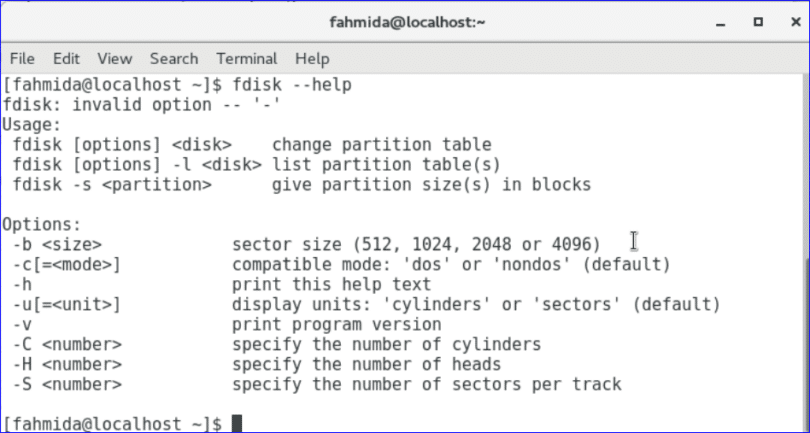
- LINUX CLEAN DISK SPACE HOW TO
- LINUX CLEAN DISK SPACE INSTALL
- LINUX CLEAN DISK SPACE FREE
- LINUX CLEAN DISK SPACE WINDOWS
Then finally I decided to run tune2fs -m0 on the file system even though I was certain that was not the cause - but it was! A little over 400G became available as it should be. or thought I had), I started to sweat and search desperately for a way to fix this issue, rebooting, trying "lsof" and that kind of stuff. Since I was certain I had freed those 5% reserved as a default in at least Fedora (and having some empty folders instead of having the files I had just copied. Plus, it can also clean application data for many popular Linux software, like Firefox, GIMP, KDE, APT, and Vim. You can use BleachBit for cleaning caches, cookies, history, and temporary files, among many others.
LINUX CLEAN DISK SPACE FREE
However, I was suddenly stuck with 0 bytes free according to df, but the difference between total and used space said something else. BleachBit is a reliable system cleaner that can save valuable disk space by deleting unnecessary files from your Linux machine. This command summarizes the space usage for a specified directory or the current directory if none is specified. RELATED: 7 Tips to Get the Most Out of BleachBit, a 'CCleaner for Linux' BleachBit is basically a CCleaner for Linux.It will scan your computer for unnecessary temporary files and automatically remove them to free up space. The second command removes obsolete packages. The first command cleans the packages from /var/cache/apt/archives.
LINUX CLEAN DISK SPACE HOW TO
Usually I free all available disk space, also the 5% reserved for root (tune2fs -m0), since it's a single user file server system. How to Check Linux Disk Space with the du Command Use the du command to analyze disk space at a more granular level. For instance, in the Debian- and Ubuntu-based systems, which use apt as the package manager, you can remove the cached update files with: sudo apt clean. rockgtr Ubuntu should have the Disk Usage Analyzer in the applications.
LINUX CLEAN DISK SPACE WINDOWS
We’ve also covered freeing up disk space on Windows and freeing up disk space on a Mac.
LINUX CLEAN DISK SPACE INSTALL
For example, the APT package manager keeps package files around even after you install them a waste of space unless you plan on uninstalling and reinstalling them. Im sure there is some 'cruft' in there I could clean out. Linux systems aren’t as light on disk space as they could be. (if I understand du -h correctly, all directories within ~ ought to be included within 165MB.One reason for missing disk space (a scenario I just encountered myself because I obviously didn't do as I normally do when creating a new array), is this. Good point I just checked my Linux Mint 19.3 desktop machine with 'Disk Usage Analyzer' and after several years of use and numerous upgrades my root folder is still only using 20GB of space. My mental math added it up to WAY less than 7gb.

As you can see, this command is going to free up 300 Mb of free space in my system. The biggest directory by far was the ~ directory containing 165MB all other were 30MB and below. It’s a no-brainer command that you can run from time to time to make some free space on your Ubuntu system: sudo apt-get autoremove. Their reported size in aggregate should not be even close to 7 gb.which is why I ask "what is taking up all that space?" When a file is deleted, its contents may still be left in the filesystem, unless explicitly overwritten with something else. To investigate what was taking so much space, I ran du -h in ~ and saw the list of all directories on the server. This can be cumbersome, so users can narrow things down by specifying the disk they are working on. As you can see, it shows every disk that is connected to the system. It should produce an output that looks like the following image. I surprised not only by how little was available/how much space was used,(I am on the /dev/xvda1 instance) but also surprised to see 2 alternative filesystems. Open the Terminal and type df, then press Enter. For instance, metadata for disabled repositories will not be affected. I deleted the csv that was partially generated from my report (it was going to be a pretty sizable one) and ran df -h and was surprised to get this output: Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on The simple command to cleanup yum caches: yum clean all Note that the above command will not remove everything related to yum. I recently ran a report on my EC2 server and was told that it ran out of space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
